bubble sort in java
problem
You wish to sort a list of numbers from the smallest to the greatest or vice versa. In this post we will see one of the sorting algorithms called Bubble Sort. Let’s suppose we have a list of 10 numbers, and wish to sort them in an ascending order.
SOLUTION
Using Bubble sort algorithm. This algorithm uses a greedy approach to the problem.
It loops the array of numbers and each time, it is getting two numbers (e.g. the number 10 and 3 below) and comparing them between them.
If the second number is smaller than the first one, it swaps them; putting the smaller first and the greater right after.
Repeating this process ends up sorting the array (in ascending order).
//the array with the unordered numbers
int[] numbers= new int[]{ 10,3,9,5,2,8,7,4,1,6};
//loop through the items
for (int i = 0; i <= numbers.length -1; i++) {
for(int k= 0; k< numbers.length-i-1; k++){
//take the first two numbers indices(k, k+1)
if(numbers[k] > numbers[k+1]){ //compare them if they're in ascending order
//swap them if not
int temp = numbers[k];
numbers[k] = numbers[k+1];
numbers[k+1] = temp;
}
} //repeat
}
//print the sorted array
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(numbers));
running
Running it, let’s put it in a main method.
import java.util.Arrays;
public class BubbleSort {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//the array with the unordered numbers
int[] numbers= new int[]{ 10,3,9,5,2,8,7,4,1,6};
//loop through the items
for (int i = 0; i <= numbers.length -1; i++) {
for(int k= 0; k< numbers.length-i-1; k++){
//take the first two numbers indices(k, k+1)
if(numbers[k] > numbers[k+1]){ //compare them if they're in ascending order
//swap them if not
int temp = numbers[k];
numbers[k] = numbers[k+1];
numbers[k+1] = temp;
}
} //repeat
}
//print the sorted array
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(numbers));
}
}
output
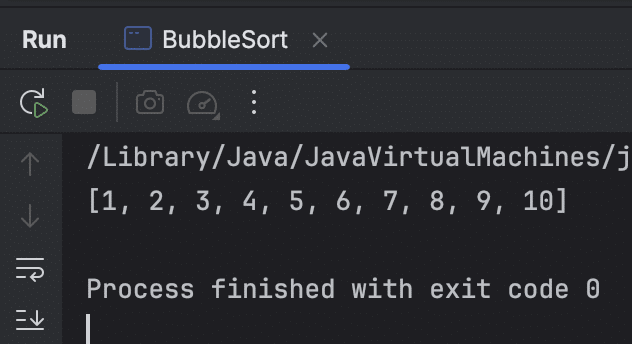
The numbers are now sorted in Ascending order from the lowest to the greatest.
Sorting in descending order
All we have to do is to change the condition when the pair of numbers are compared, as shown below:
if(numbers[k] < numbers[k+1]){ //compare them if they're in descending order
The full code:
import java.util.Arrays;
public class BubbleSort {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//the array with the unordered numbers
int[] numbers= new int[]{ 10,3,9,5,2,8,7,4,1,6};
//loop through the items
for (int i = 0; i <= numbers.length -1; i++) {
for(int k= 0; k< numbers.length-i-1; k++){
//take the first two numbers indices(k, k+1)
if(numbers[k] < numbers[k+1]){ //compare them if they're in descending order
//swap them if not
int temp = numbers[k];
numbers[k] = numbers[k+1];
numbers[k+1] = temp;
}
} //repeat
}
//print the sorted array
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(numbers));
}
}
output
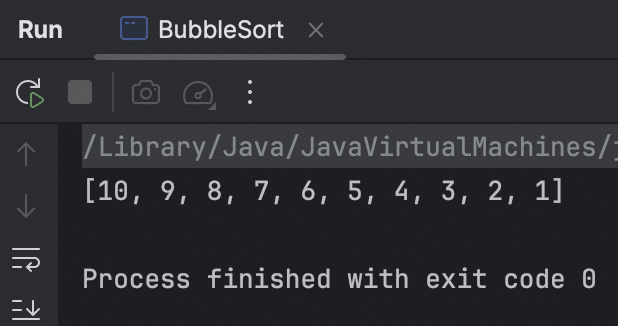
conclusion
In this post, we saw how to use the Bubble Sort algorithm to sort a small array of numbers. This algorithm can easily be modified to sort numbers in ascending or descending just by changing the boolean expression in the if statement.
Share it!
Ellion
Professional IT consultant, writer, programmer enthusiast interested in all sorts of coding.
Eats all cookies 🍪
