Using RestTemplate in Spring boot
problem
You wish to quickly send an Http Request, for example to an API and get back its response. In this post we’re gonna use the https://www.themealdb.com/ API for testing purposes and because I like it.
SOLUTION
Using the RestTemplate object.
In Spring boot, we can autowire the RestTemplate and perform http requests by using an endpoint.
First, let’s create a @Bean configuration for the RestTemplate as follows:
@Bean
public RestTemplate restTemplate(RestTemplateBuilder builder) {
return builder.build();
}
I placed that in the main class that runs the Spring Boot application, for example:
package com.programmerabroad.resttemplate;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.web.client.RestTemplateBuilder;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.web.client.RestTemplate;
@SpringBootApplication
public class ResttemplateApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(ResttemplateApplication.class, args);
}
@Bean
public RestTemplate restTemplate(RestTemplateBuilder builder) {
return builder.build();
}
}
Setting the Api url in the application properties and later loading it using the @Value annotation.
spring.application.name=resttemplate
themealdb.url=https://www.themealdb.com/api/json/v1/1/search.php?s=
I’m using the RestTemplate to send the HttpRequest to the API:
String url = this.apiUrl + search;
ResponseEntity<String> forEntity = restTemplate.getForEntity(url, String.class);
return forEntity.getBody();
Simply the getForEntity() method is doing all the job in one line.
Then I get the response which is a JSON object. The full code as follows:
package com.programmerabroad.resttemplate;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus;
import org.springframework.http.MediaType;
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;
import org.springframework.web.client.RestTemplate;
@RestController
public class ApiController {
@Autowired
private RestTemplate restTemplate;
@Value("${themealdb.url}")
private String apiUrl;
@GetMapping(value = "/", produces = MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_VALUE)
public String index(@RequestParam(name = "search") String search) {
String url = this.apiUrl + search;
ResponseEntity<String> forEntity = restTemplate.getForEntity(url, String.class);
return forEntity.getBody();
}
}
output
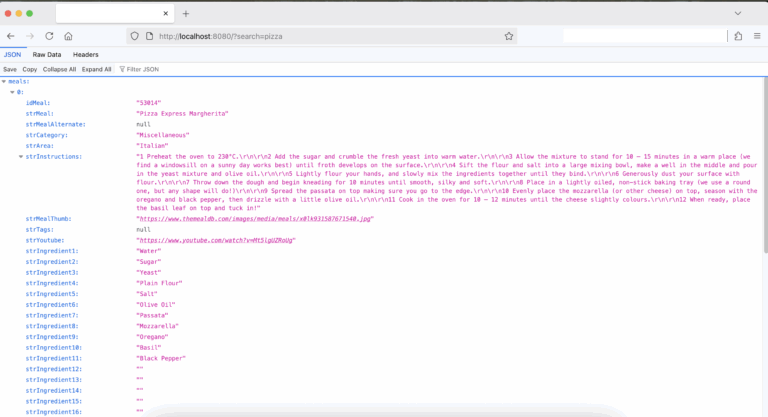
Mapping the JSON response to an object - DTO
We can create a DTO – Data Transfer Object that will be responsible for representing the JSON from the API into an object in the Java world. It’s simply a class that contains all the fields according to the keys in the JSON.
For example:
package com.programmerabroad.resttemplate;
import java.io.Serializable;
public class MealDto implements Serializable {
public String idMeal;
public String strMeal;
public Object strMealAlternate;
public String strCategory;
public String strArea;
public String strInstructions;
public String strMealThumb;
public String strTags;
public String strYoutube;
public String strIngredient1;
public String strIngredient2;
public String strIngredient3;
public String strIngredient4;
public String strIngredient5;
public String strIngredient6;
public String strIngredient7;
public String strIngredient8;
public String strIngredient9;
public String strIngredient10;
public String strIngredient11;
public String strIngredient12;
public String strIngredient13;
public String strIngredient14;
public String strIngredient15;
public String strIngredient16;
public String strIngredient17;
public String strIngredient18;
public String strIngredient19;
public String strIngredient20;
public String strMeasure1;
public String strMeasure2;
public String strMeasure3;
public String strMeasure4;
public String strMeasure5;
public String strMeasure6;
public String strMeasure7;
public String strMeasure8;
public String strMeasure9;
public String strMeasure10;
public String strMeasure11;
public String strMeasure12;
public String strMeasure13;
public String strMeasure14;
public String strMeasure15;
public String strMeasure16;
public String strMeasure17;
public String strMeasure18;
public String strMeasure19;
public String strMeasure20;
public String strSource;
public Object strImageSource;
public Object strCreativeCommonsConfirmed;
public Object dateModified;
}
Because our search result in the API can return more than one results (meals) we need another one DTO class to hold a list of the meals.
For example:
package com.programmerabroad.resttemplate;
import java.io.Serializable;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class RootDto implements Serializable {
public ArrayList<MealDto> meals;
}
Change the controller to adopt the change:
@GetMapping(value = "/", produces = MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_VALUE)
public ResponseEntity<RootDto> index(@RequestParam(name = "search") String search) {
String url = this.apiUrl + search;
ResponseEntity<RootDto> forEntity = restTemplate.getForEntity(url, RootDto.class);
return forEntity;
}
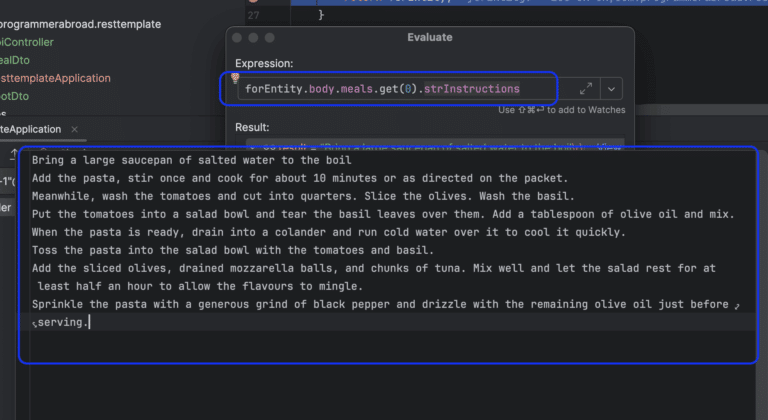
For example, we can retrieve only the instructions of making a meal, e.g. pasta.
forEntity.body.meals.get(0).strInstructions
Simply by accessing the field strInstructions above we can see the instructions as String.
output
conclusion
In this post we saw how to use the RestTemplate object given by Spring Boot and how to hit the API of themealdb.com and get a JSON response to our web browser. Also, we saw how to easily map the JSON response to a Java object POJO/ DTO for more organized information.
Share it!
Ellion
Professional IT consultant, writer, programmer enthusiast interested in all sorts of coding.
Eats all cookies 🍪
